Using ssh key allows you to work with private repos easily without username password authentication. Github now has an option for PAT (personal access token, read about it here), but I still use ssh key option.
Step-1: Install Git
Mac/Linux: git should be pre-installed.
Windows: download and install git bash from here.
Step-2: Generate a new ssh rsa key
If you already have a rsa key pair, skip this step and use the same keys. Otherwise, use below command to generate a new public-private key pair. Works on windows, mac and linux.
Replace youremail@something.com with your github email id.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "youremail@something"Notice it’s capital C .
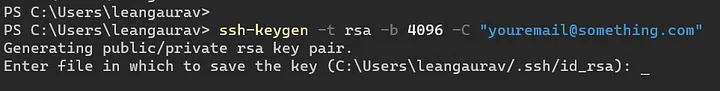
When asked for location and file name, hit enter to save to default location.
When asked for passphrase, either type a secret passphrase and hit Enter, or to leave empty hit Enter twice.
This generates 2 files:
- A public key ending with
.pub - A private key without any extension (this is secret and should never be shared)
Step-2.1: Add key to ssh agent (for windows only)
Open git bash
Run this command (Use Shift + Ins to paste in bash)
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"You’ll see the process id
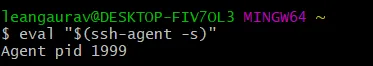
Add the newly generated key to ssh agent. (Use the same file which was generated in previous step)
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Step-3: Add ssh key to github
Copy the newly generated public key
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubAbove command works on Mac and Linux. On windows it works in powershell and git-bash. Copy the printed output as it is, including the starting ssh-rsa .
Now go to this url https://github.com/settings/keys
Or manually navigate:
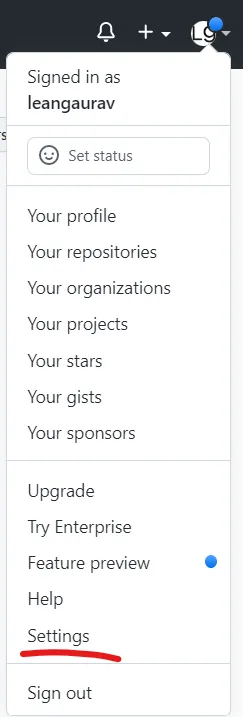
1. click top right profile icon -> settings
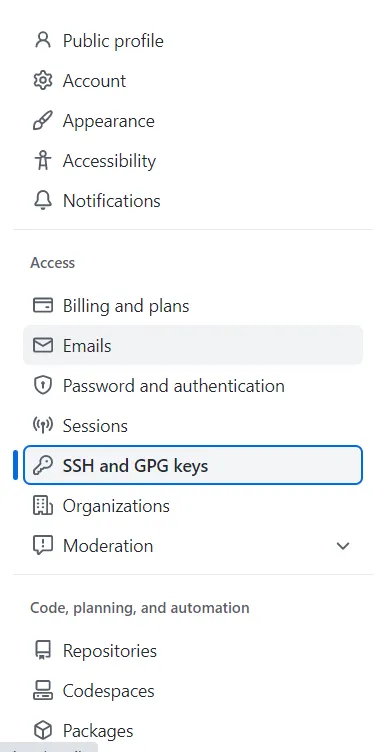
2. Click “ssh and gpg keys” in left panel
3. Click New SSH key
4. Add Titleof your choice -> leave the Key type set to Authentication Key -> Paste the copied public key in Key section
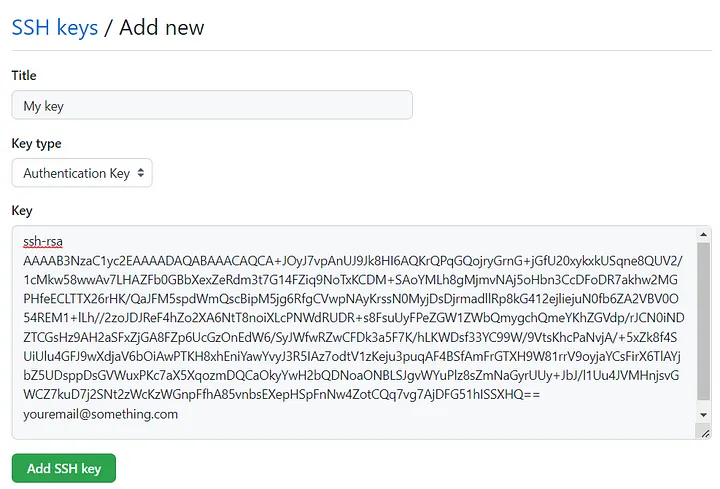
Hit the green button.
Done 🙌🏻
You should be able to clone, pull-push to private repos with the ssh remote url.
